Gaper pea crab • Pinnixa littoralis
|
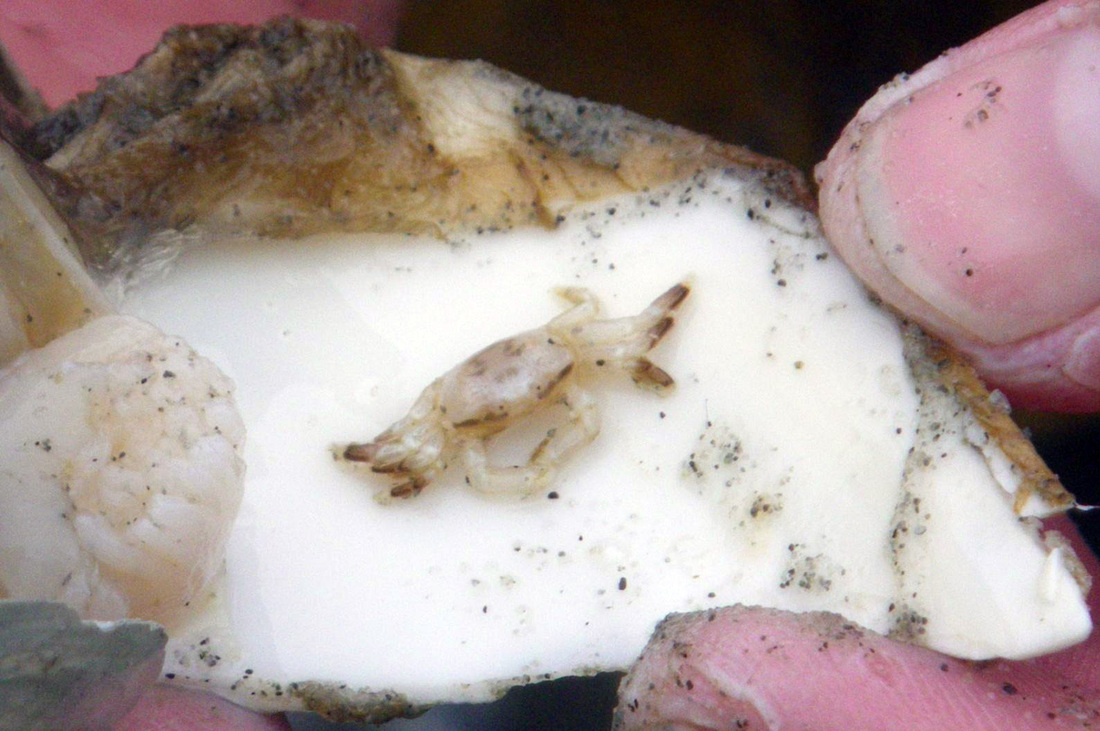
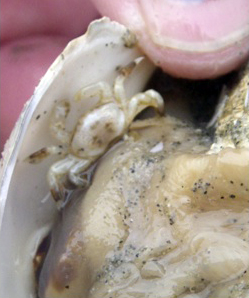
Gaper pea crab found in a fat gaper (Tresus capax). Photos by Thalia Christou (left) and Stuart Higgs.
|
Identification
The gaper pea crab is a small white crab that lives in the fat gaper (Tresus capax). The carapace of the female gets to 27 mm across; the carapace of the male is smaller at 18 mm maximum. The male often bears dark markings.
Habitat & Range
The gaper pea crab lives commensally in the mantle cavity of the fat gaper, a relatively large bivalve, in the intertidal and subtidal to a depth of 91 m. Fat gapers bury in sandy, muddy, and clay substrates in sheltered locations. Pea crabs are usually found in pairs inside their host. The range of the gaper pea clam stretches from central Alaska (Prince William Sound) to northern Mexico (Bahia Santa Maria). It is widespread along the British Columbia coastline.
Similar Species
The mantle pea crab (Pinnixia faba) also lives in the fat caper and can be difficult to distinguish from the gaper pea crab. There is a gape in the closed claws of the female gaper pea crab but not in the female mantle pea crab. The male gaper pea crab has a longer third walking leg than the male mantle pea crab. The mantle pea crab has a tooth near the base of the movable portion of its claw. The mantle pea crab is more common in British Columbia.
iNaturalist
https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/459537-Pinnixa-littoralis
The gaper pea crab is a small white crab that lives in the fat gaper (Tresus capax). The carapace of the female gets to 27 mm across; the carapace of the male is smaller at 18 mm maximum. The male often bears dark markings.
Habitat & Range
The gaper pea crab lives commensally in the mantle cavity of the fat gaper, a relatively large bivalve, in the intertidal and subtidal to a depth of 91 m. Fat gapers bury in sandy, muddy, and clay substrates in sheltered locations. Pea crabs are usually found in pairs inside their host. The range of the gaper pea clam stretches from central Alaska (Prince William Sound) to northern Mexico (Bahia Santa Maria). It is widespread along the British Columbia coastline.
Similar Species
The mantle pea crab (Pinnixia faba) also lives in the fat caper and can be difficult to distinguish from the gaper pea crab. There is a gape in the closed claws of the female gaper pea crab but not in the female mantle pea crab. The male gaper pea crab has a longer third walking leg than the male mantle pea crab. The mantle pea crab has a tooth near the base of the movable portion of its claw. The mantle pea crab is more common in British Columbia.
iNaturalist
https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/459537-Pinnixa-littoralis
References
Adams, M. J. (2005). Pinnixa sp. (Gaper pea crabs). Beach Watchers. Washington State University. Accessed 28/01/2015.
Hart, J. Pinnixa littoralis Holmes, 1894. In Klinkenberg, Brian. (Ed.) E-Fauna BC: Electronic Atlas of the Fauna of British Columbia. Lab for Advanced Spatial Analysis, Department of Geography, University of British Columbia, Vancouver. Accessed 28/01/2015.
Jensen, G.C. (1995). Pacific Coast Crabs and Shrimp. Monterey, CA: Sea Challengers. P.
Lamb, A., and Hanby, B. (2005). Marine Life of the Pacific Northwest [electronic version]. Madeira Park, BC: Harbour Publishing.
Authors and editors of page
Kelly Fretwell and Brian Starzomski (2015).
Adams, M. J. (2005). Pinnixa sp. (Gaper pea crabs). Beach Watchers. Washington State University. Accessed 28/01/2015.
Hart, J. Pinnixa littoralis Holmes, 1894. In Klinkenberg, Brian. (Ed.) E-Fauna BC: Electronic Atlas of the Fauna of British Columbia. Lab for Advanced Spatial Analysis, Department of Geography, University of British Columbia, Vancouver. Accessed 28/01/2015.
Jensen, G.C. (1995). Pacific Coast Crabs and Shrimp. Monterey, CA: Sea Challengers. P.
Lamb, A., and Hanby, B. (2005). Marine Life of the Pacific Northwest [electronic version]. Madeira Park, BC: Harbour Publishing.
Authors and editors of page
Kelly Fretwell and Brian Starzomski (2015).